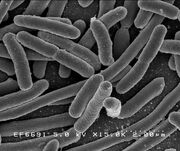
E. coli under an electron microscope, courtesy NIH
Escherichia coli, usually abbreviated E. coli is a common bacteria that is usually found in the intestines of all warm blooded animals where they actually aid in digestion. E. coli also helps the body synthesize Vitamin K and can keep harmful bacteria from establishing themselves in the digestive tract. Although most strains of this bacteria are harmless, some strains can lead to food poisoning in humans. They are always found in stool and the presence of E. coli in an environment can often determine if it's contaminated by feces.
Because of its well established genetic structure, E. coli is the bacteria of choice for experimental gene splicing.
Some of the diseases that can be caused by harmful strains of the bacteria are gastroenteritis, urinary tract infection, neonatal meningitis, peritonitis, septicemia, and pneumonia. These are common when humans consume food or water contaminated by fecal matter.
